Chronic Kidney Disease
Background
- A third of Americans are at risk of Chronic kidney disease, and age is one of the major factors. Over a half of Americans older than 75, are believed to have some sort of kidney damage.
Shape
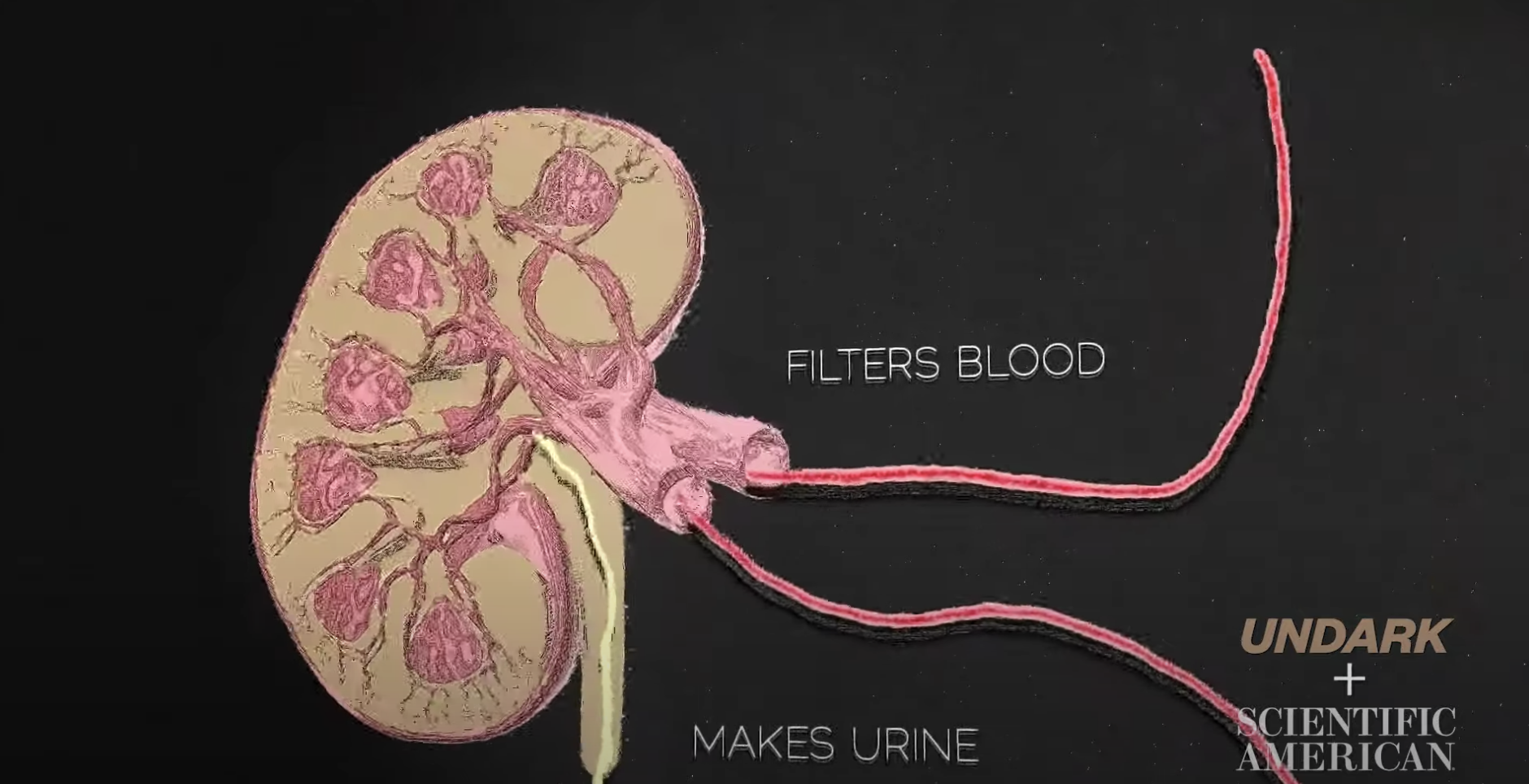
- Kidneys are two bean-like organs that sit just below rib cage near the spine.
Functionality
- It keeps balance of potassium, sodium and other minerals in the body fluid, and expels waste as urine out of the body.
What will happen when it fails?
- Nerves, muscles and other tissues stop working normally and can eventually fail without this balance. This is called Chronic Kidney Disease, and is growing global wide,
What is dialysis?
- Dialysis helps solve the occurred problem when there is a kidney failure. It cleans the fluid and maintain a safe level of sodium and potassium and other chemicals in the blood.
- Dialysis could not cure patient with kidney failure, but it will keep them alive for organ transplant wherever life takes them - though disparities abound, especially in the U.S.
Types of dialysis
- There are two major types of dialysis. One is hemodialysis, which uses an artificial kidney out of your body to filter the blood. The other is peritoneal dialysis, which uses the lining of your own abdomen as a natural filter, and pump fluid in and out via catheter.
Commercial development of dialysis
- The for-profit dialysis industry has been developing since 1970s. 80% of the market is dominated by two massive companies. Critics say that it would be hard for small firm to survive, hindering innovation.
- Some studies suggest that after large corporation buys small dialysis facilities, the hospitalizations go up, and the quality goes down.
Summary
- For patients, there is only one way to go - stay in the system, stay on dialysis, wait for a kidney - or die.
Ref: What Is Chronic Kidney Disease, and How Might It Affect You?